What's MES?
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is a software solution designed to monitor, track, document, and control the entire manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished products. MES plays a crucial role in optimizing production operations by providing real-time visibility and control over various elements of the manufacturing process, including inputs, personnel, machines, and support services.
Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is the information system used in production environments to track the transformation of Raw Materials to Finished Product to make SMART business decisions.
Key Functions of MES
- Real-Time Monitoring: MES captures and analyzes data from machines, sensors, and operators, enabling manufacturers to understand current production conditions and optimize processes accordingly.
- Production Tracking: It tracks the transformation of raw materials into finished goods, providing a comprehensive view of production activities and ensuring that operations align with planned schedules.
- Quality Control: MES enforces quality control procedures and monitors metrics to ensure that products meet required standards. Immediate feedback allows for quick adjustments to minimize defects and waste.
- Resource Management: The system helps manage production resources, including materials, labor, and equipment, to ensure efficient utilization and minimize downtime.
- Integration with ERP Systems: MES often integrates with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, enhancing the flow of information across departments and aligning business operations with manufacturing activities.
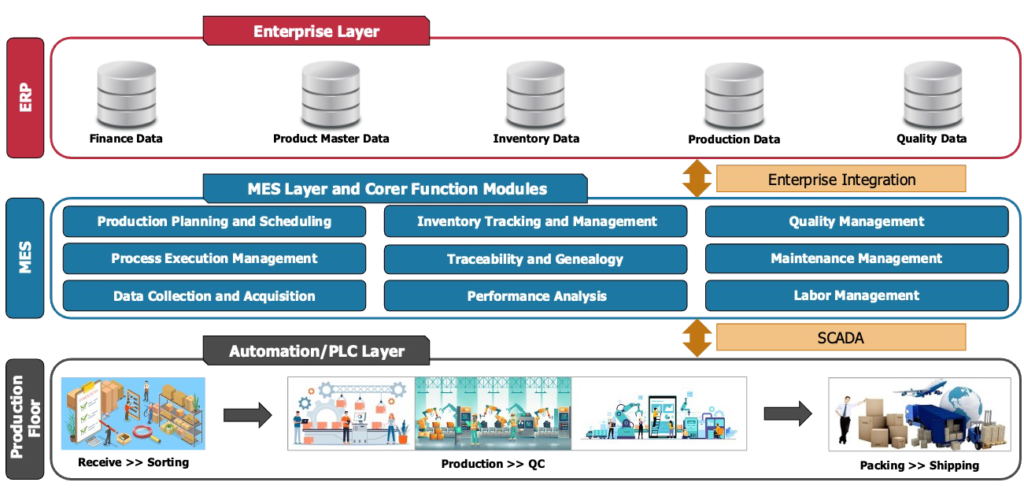
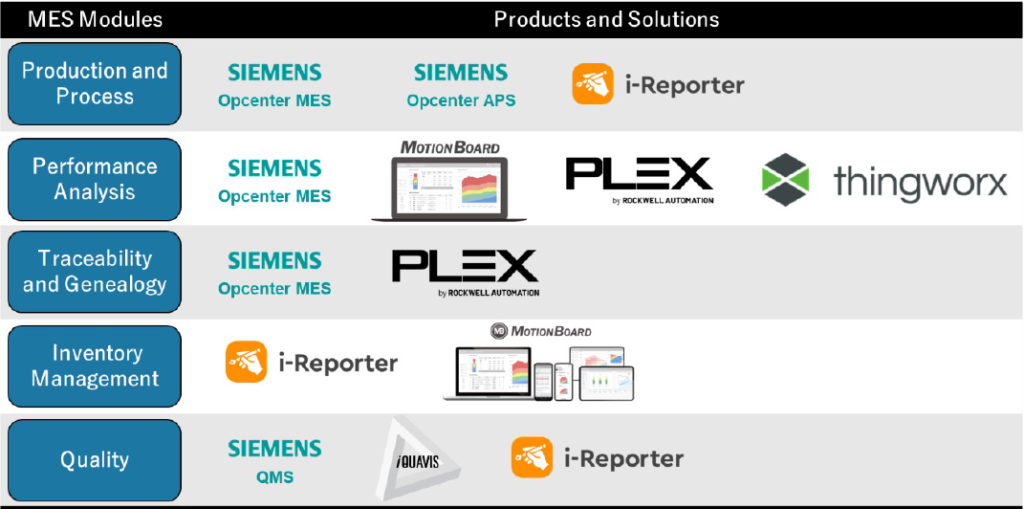
1. Production Planning & Scheduling
- Visualize production plans in real-time and optimize capacity and resources
- Share schedules with shop floor employees immediately
- Create production orders manually or download from ERP automatically
- Track tool handovers, machine changeovers, and material changes
- Eliminate dependency on complicated capacity scheduling systems
- Assess ability to meet deadlines and get a 360-degree view of manufacturing capacity
- Generate optimal sequence of production orders for the line
2. Process Execution Management
- Monitor process routings and redefine better alternatives
- Provide work instructions to assist technicians
- Track end-to-end progress of each job
- Trigger alerts for out-of-spec asset conditions
- Provide centralized control of the factory floor
- Dispatch production jobs without delays
3. Data Collection and Acquisition
- Collect real-time data from various automated processes
- Utilize IoT standards to enable data collection with minimal operator support
- Provide a centralized digital logbook to eliminate manual data entry
- Extract data from any point of the manufacturing process in real-time
4. Inventory Tracking and Management
- Manage work-in-progress (WIP) inventory across production stages
- Integrate with ERP to automatically validate inventory levels at each stage
- Eliminate manual verification of WIP inventory locations
5. Traceability and Genealogy
- Document batches and individual products from raw materials to finished goods
- Provide complete history of each unit and trace its path through production
- Integrate with SCADA to trigger alarms when units are out of specification
6. Performance Analysis
- Calculate overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
- Analyze actual run time, performance rate, and quality rate
- Compare real-time production to historical data and scheduled goals
7. Quality Management
- Ensure consistent product creation methods from batch to batch
- Easily update recipes to add new products or adjust specifications
- Reduce waste while streamlining processes through recipe management
8. Maintenance Management
- Track equipment maintenance and downtime
- Schedule preventive maintenance activities
- Maintain equipment performance and availability
9. Labor Management
- Maintain employee profiles to assess and match skills
- Record labor hours for wage calculation
- Monitor employee attendance and productivity
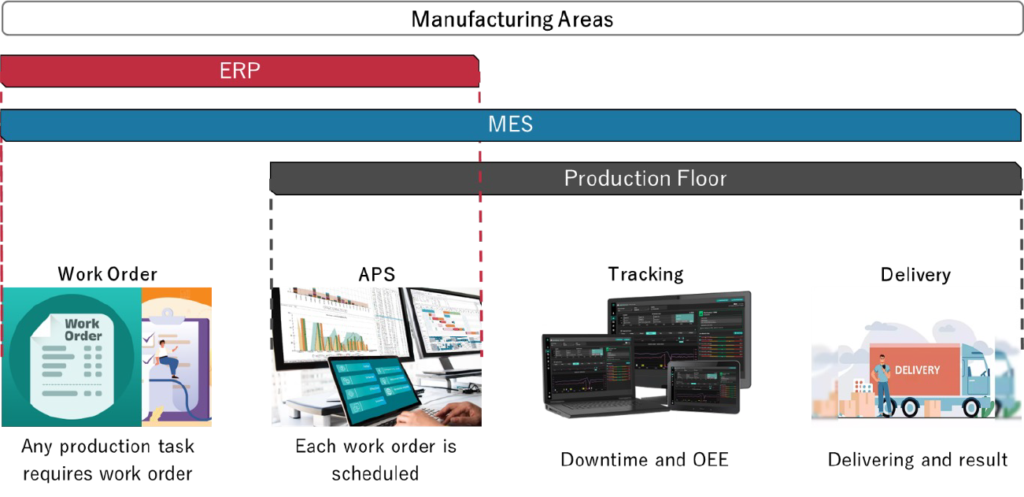
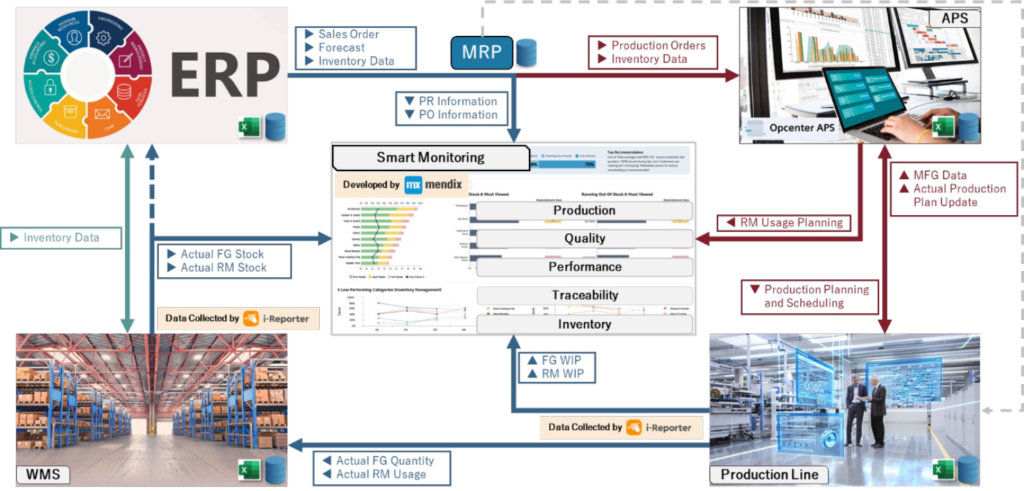
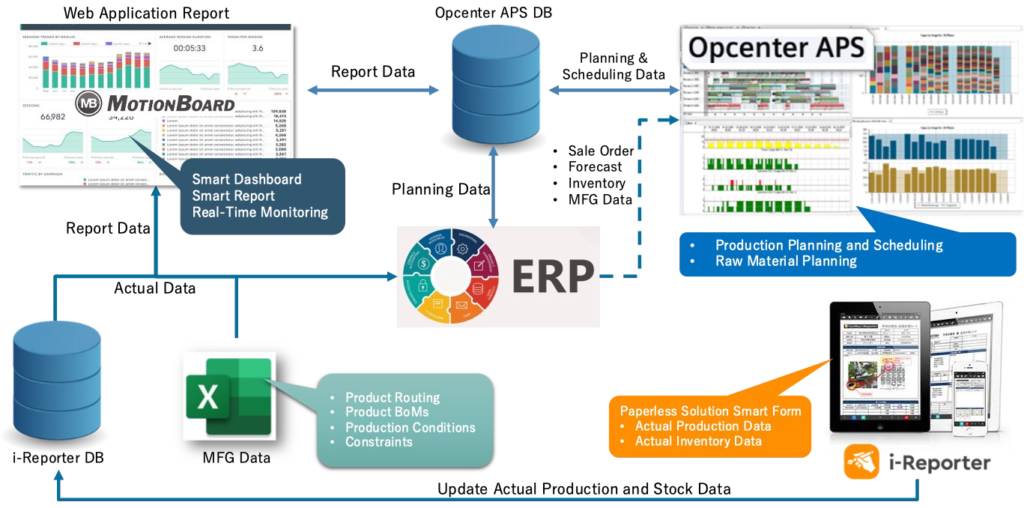
MES Architecture and Integration
MES sits between the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system at the business level and the process control systems on the factory floor. It integrates with other manufacturing systems like:
- ERP: Aligning business operations with production activities
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Exchanging product definitions, routings and work instructions
- Warehouse Management System (WMS): Managing material availability, staging and deliveries
- Maintenance Management System: Tracking equipment performance and maintenance
This integration enables the flow of information across departments for enhanced efficiency and productivity. MES is a critical software layer that provides real-time monitoring, control and optimization of production processes to improve manufacturing performance and quality.
Benefits of using MES in manufacturing
The implementation of a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) in manufacturing operations offers several significant benefits that enhance efficiency, quality, and overall performance. Here are the main advantages:
- Improved Production Efficiency: MES provides real-time visibility into production processes, enabling manufacturers to track operations and identify bottlenecks. This leads to optimized workflows, reduced downtime, and increased productivity through automation of scheduling and adjustments based on demand.
- Enhanced Quality Control: With real-time data on production metrics, MES allows for immediate identification and correction of quality issues. This capability helps reduce defects, scrap, and rework, ultimately improving product quality and customer satisfaction.
- Real-time Data and Analytics: MES systems collect and analyze data continuously, providing insights into key performance indicators (KPIs) such as production rates and cycle times. This data-driven approach facilitates informed decision-making, predictive maintenance, and proactive issue resolution.
- Inventory Management and Supply Chain Optimization: MES enables real-time tracking of inventory levels, which helps minimize excess stock and waste. By managing material flow efficiently, manufacturers can reduce costs and improve supply chain visibility, ensuring that the right materials are available when needed.
- Regulatory Compliance: For industries with strict regulatory requirements, MES helps maintain compliance by ensuring proper documentation and traceability of production processes. This is crucial for sectors like pharmaceuticals and food and beverage, where adherence to standards is mandatory.
- Reduced Lead Times and Costs: By streamlining operations, MES minimizes order lead times and lowers labor costs through automation and improved resource management. This efficiency contributes to higher profitability and competitiveness in the market.
- Paperless Operations: The transition to a digital MES reduces reliance on paperwork, lowering the risk of human error and facilitating immediate access to critical data across the organization. This shift enhances operational transparency and communication among team members.
Adopting an MES can significantly transform manufacturing operations by improving efficiency, quality, and responsiveness, ultimately leading to increased profitability and customer satisfaction.