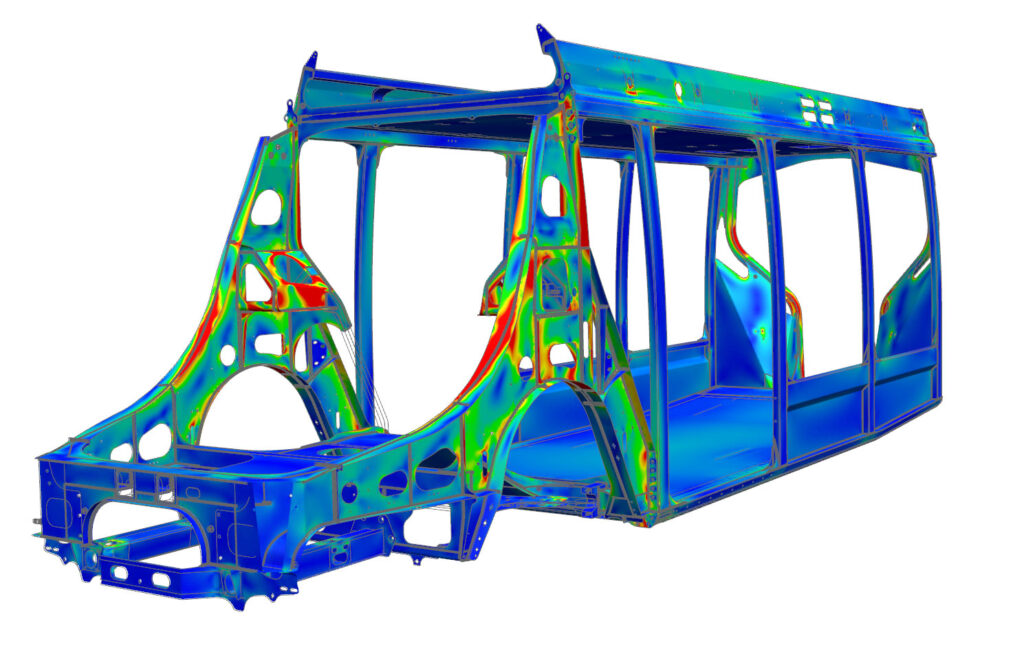
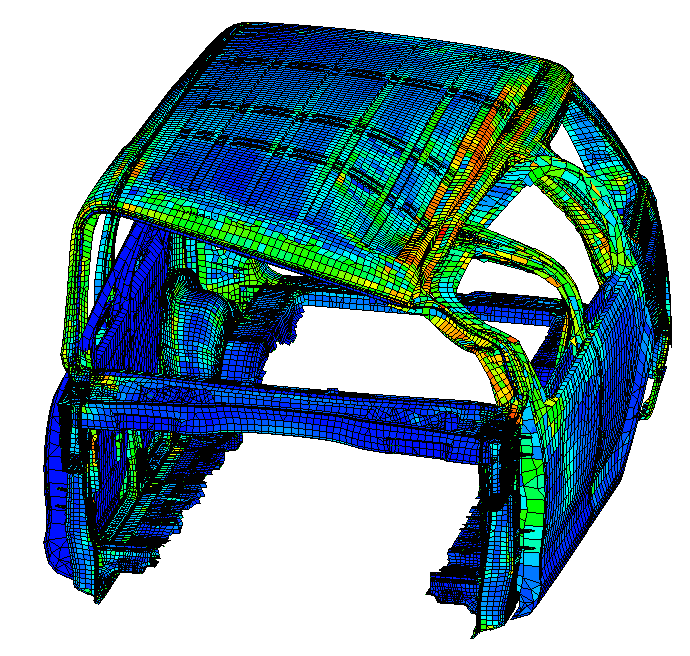
How Structural Analysis is Done ?
1.Model Preparation
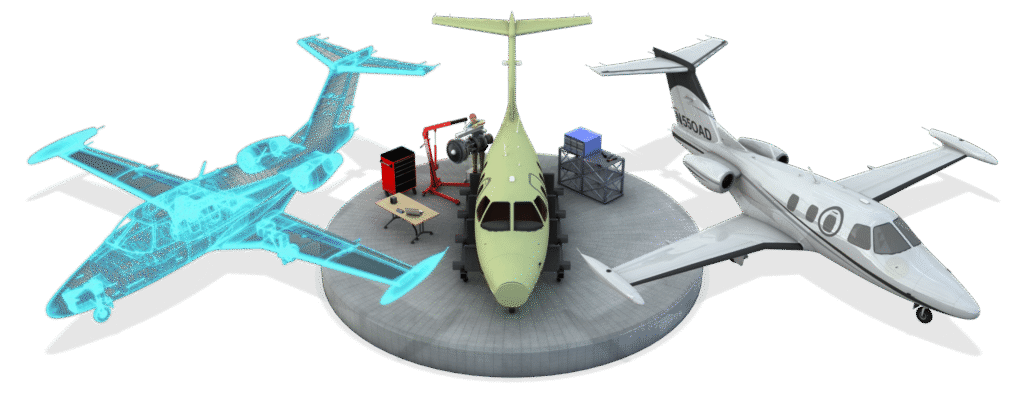
Import geometry from CAD or create simplified models.
Clean up and define materials, properties, and connections.
2.Meshing (except in meshless tools like SIMSOLID)
Discretize the model into finite elements for numerical analysis.
3.Load & Boundary Conditions
Apply forces, pressures, thermal effects, constraints, and contacts that replicate real-world conditions.
4.Solver Execution
Use the selected solver (OptiStruct, RADIOSS, Nastran, etc.) to calculate structural responses under defined conditions.
5.Post-Processing & Interpretation
Visualize results such as stresses, strains, displacements, vibration modes, and failure points.
Optimize design based on insights.
Benefits of Structural Analysis Tools
Reduce Physical Testing: Minimize prototypes, saving cost and time.
Improve Design Reliability: Identify weaknesses early in the design cycle.
Support Innovation: Enable lightweighting and material optimization.
Speed to Market: Accelerate decision-making with virtual validation.

Who needs Structural Analysis ?
Engineers and Manufacturers who need to reduce number of prototyping
Engineers who need better product performance and life cycle